Scientific activities
The ESD members have experience supported by scholarly achievements in the field of designed research documented with an array of publications in renowned scientific journals, participation in national (NSC, EIRU) and international (AvH, DAAD, EU) research projects, invited lectures at international scientific conferences and research institutes. The members of the Division have a wide range of skills and experience in constructing and operating science and research equipment as well as credentials obtained in the country and as part of scientific internships at such research centres as: Universität Zürich-Irchel; CERN (the NA61 SHINE experiment), Geneva; Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH; Fritz-Haber Institut der Max-Planck Gesellschaft, Berlin; Institut für Physikalische und Theoretische Chemie, Universität Bonn; Physik-Institut, Dipartimento di Scienze Chimiche, Università degli Studi di Padova; Università degli Studi di Roma “Tor Vergata”; Université Libre de Bruxelles; ISA, University of Aarhus. Moreover, the members of the Division have many years of experience in research and development (R+D) activities as part of occupying posts at the institutions: WRC EIT+ and Łukasiewicz PORT.
The research conducted in the ESD concern the physicochemical properties of solid surfaces in the environment of ultra high vacuum (UHV) and electrochemical (EC). The Department operates laboratories equipped with high vacuum equipment and an electrochemical laboratory. In addition to primary research, the division also conducts applied research.
Research topics
In particular the research topics include:
- chemical composition of the surface and near-surface layers of solids (metals, semiconductors, oxides, 2D materials),
- adsorption and determining the mechanism of adsorbate growth (metals, semiconductors, inorganic and organic molecules),
- structures (near- and long-range) of surfaces, near-surface layers and adsorbate layers,
- desorption and thermal stability of adsorbates,
- surface morphology on the nanometer scale,
- liquid-solid and gas-solid phase systems,
- electrode reactions of oxidation and reduction (RedOx),
- deposition of metal ions and molecules from solutions on the surfaces of monocrystalline electrodes.
Experimental methods
The research uses such experimental methods as:
- Auger electron spectroscopy (AES),
- X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS),
- ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS),
- directional Auger electron spectroscopy (DAES),
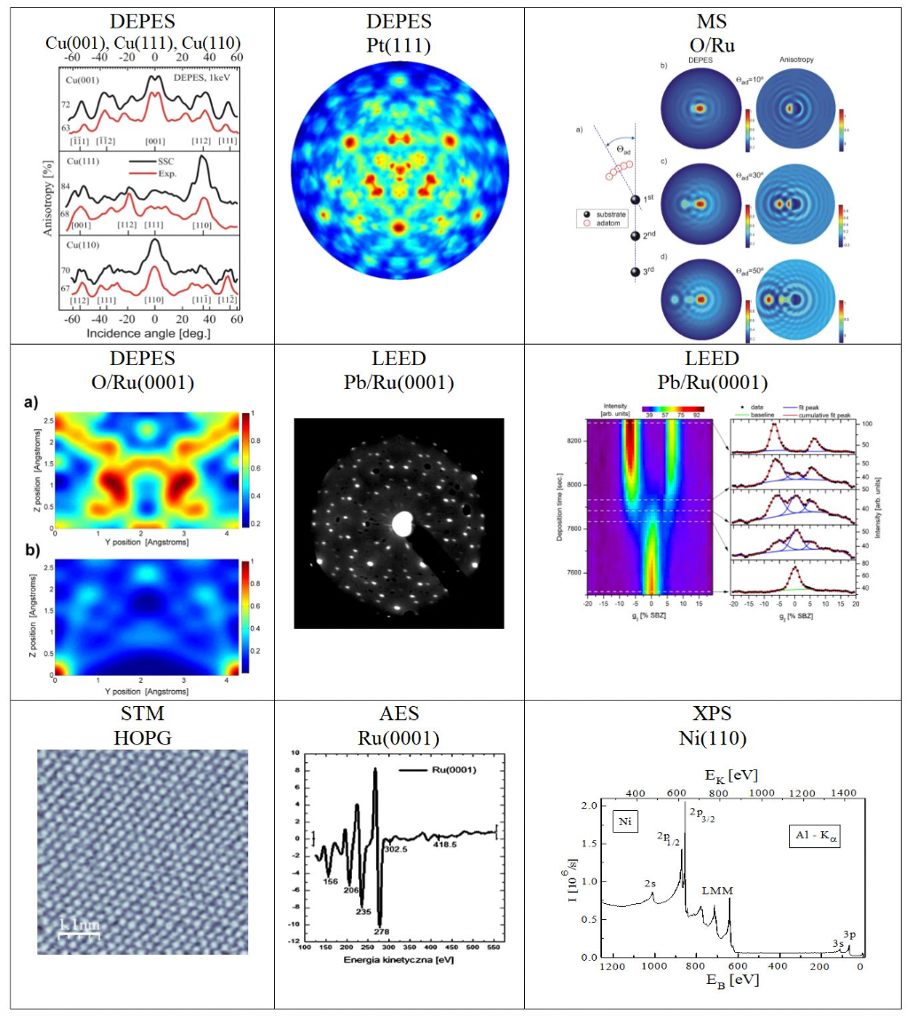
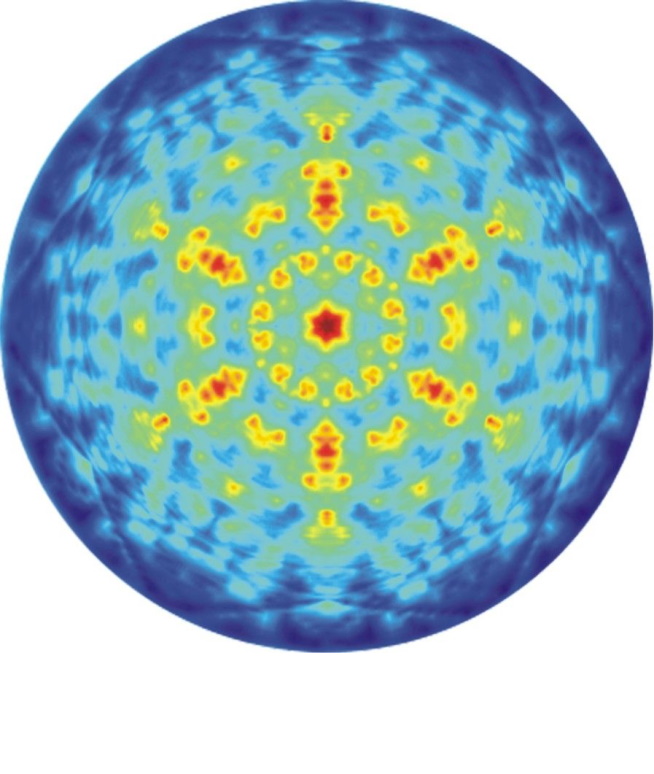
- directional elastic peak electron spectroscopy (DEPES),
- low-energy electron diffraction (LEED, IV-LEED),
- mass spectrometry (MS),
- scanning tunneling microscopy (UHV STM, EC-STM),
- measuring changes in output operation (Δϕ)
- cyclic voltammetry (CV).
Numerical methods
The ESD also conducts numerical calculations for simulating electron scattering processes in crystalline samples and obtaining theoretical DAES and DEPES results using multiple scattering (MS) theory. By comparing experimental and theoretical results, both qualitative and quantitative information about the structure of adsorption systems is obtained.
Sample results: